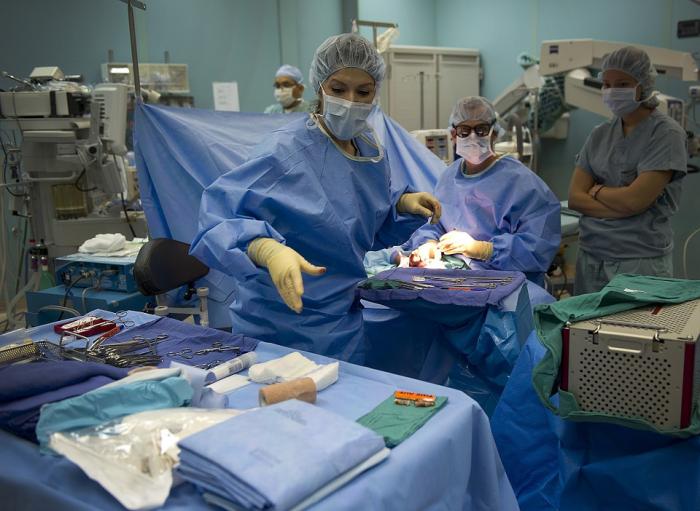
Hysteroscopy Surgery in Indore
Hysteroscopy gets its name from the tool used to view the womb. This tool is called a hysteroscope.
Many gynecological operations can be performed with the endoscopic technique. A hysteroscopy is a procedure used to examine the inside of the womb, hysteroscopy usually takes 30 to 45 minutes and is done as an outpatient procedure.
Hysteroscopy may be performed in women who have an abnormal Pap test, abnormal uterine bleeding, or postmenopausal bleeding. It may be used to help diagnose causes of infertility or repeated miscarriages.
The hysteroscope has special channels which allow the obstetrician to pass various instruments into the uterus. This means that as well as being able to look inside the uterus, the doctor can perform certain procedures.
-
Intra Uterine Septum
 A uterine septum is a form of a congenital malformation where the uterine cavity is partitioned by a longitudinal septum; the outside of the uterus has a normal typical shape. The wedge-like partition may involve only the superior part of the cavity resulting in an incomplete septum or a subseptate uterus, or less frequently the total length of the cavity (complete septum) and the cervix resulting in a double cervix.
A uterine septum is a form of a congenital malformation where the uterine cavity is partitioned by a longitudinal septum; the outside of the uterus has a normal typical shape. The wedge-like partition may involve only the superior part of the cavity resulting in an incomplete septum or a subseptate uterus, or less frequently the total length of the cavity (complete septum) and the cervix resulting in a double cervix.
-
Intrauterine Polyp
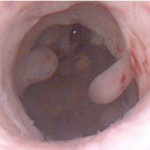 An endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They may have a large flat base (sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle (pedunculated). Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones.
An endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They may have a large flat base (sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle (pedunculated). Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones.
-
Intrauterine Myoma
 A myoma, commonly known as a fibroid, is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops in or around the uterus. Fibroids are medically known as leiomyomas and are tumors of the smooth muscle, the tissue that normally makes up that wall of theuterus.
A myoma, commonly known as a fibroid, is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops in or around the uterus. Fibroids are medically known as leiomyomas and are tumors of the smooth muscle, the tissue that normally makes up that wall of theuterus.
-
Cornual Cannulation
 The Novy Cornual Cannulation Set is intended for use through the operating channel of a hysteroscope or other uterine access device, for hysteroscopic or fluoroscopic selective catheterization and cannulation of the proximal fallopian tube(s), followed by the introduction of chromotubation solution or contrast medium, in the evaluation of tubal patency.
The Novy Cornual Cannulation Set is intended for use through the operating channel of a hysteroscope or other uterine access device, for hysteroscopic or fluoroscopic selective catheterization and cannulation of the proximal fallopian tube(s), followed by the introduction of chromotubation solution or contrast medium, in the evaluation of tubal patency.
